An AI Strategy is a Dangerous Distraction
The Acceleration of AI Demands More than an AI Strategy. It Calls for a Redesign of Your Entire Business Strategy and a Reinvention of Your Business Model
The Urgency of Disciplined Business Strategy in an AI-Driven World
Artificial intelligence (AI) is advancing at an extraordinary speed, revolutionizing industries worldwide. However, countless organizations still treat AI as just another tool in their toolkit, missing its potential as a game-changing force that requires fundamentally reevaluating their corporate strategies. Do you know the possible outcome? Expensive investments in AI that fail to generate genuine competitive advantages leave organizations lagging behind the curve.
AI is not merely another technological wave but a fundamental shift redefining industries, business models, and competitive dynamics. Organizations that automate existing processes without reconsidering their strategic choices will be left behind.
This newsletter introduces a comprehensive framework for reassessing corporate strategy in the AI era. Executive teams can systematically rethink their business models and competitive positioning by drawing from five critical strategy tools: Playing to Win (PTW), Business Model Generation, The Four Waves of AI, the Economics of AI, and Lean & Hypothesis-Driven Strategy.
The Four Paths to AI Adoption
Organizations have traditionally followed one of four paths when adopting new technology, and AI is no exception. The paths I outline below loosely align with Everett Rogers’ framework for the diffusion of innovations. Still, I needed more descriptive categories to reflect the mindsets driving organizations as they embrace new technology.[i] Organizations are likely to follow one of these four paths:
1. Reactive Adoption
Many organizations will implement AI late, often as a defensive response to competitors or regulatory changes. These organizations will struggle with fragmented initiatives and a lack of strategic alignment.
2. Tactical Implementation (The "Horseless Carriage" Syndrome)
Most organizations will believe they are proactively adopting AI but will incrementally apply it to improve efficiency while failing to rethink their business models. This mirrors how traditional retailers initially viewed e-commerce as just an additional sales channel instead of completely reinventing the shopping experience.
3. Strategic Reinvention
A minority of organizations will use AI to fundamentally rethink their business models, value propositions, and core capabilities. For example, Netflix reinvented itself from a DVD rental service into a global streaming giant powered by AI-driven recommendations.
4. Ecosystem Builders
A few organizations will leverage AI to create new platforms and industry standards. These organizations will adapt to AI and shape their industry’s evolution through it. For example, Apple reshaped the music industry with mobile through iTunes and then Apple Music.
Executive teams must ask: Are we reacting, incrementally improving, or are we fundamentally rethinking how we compete with AI?
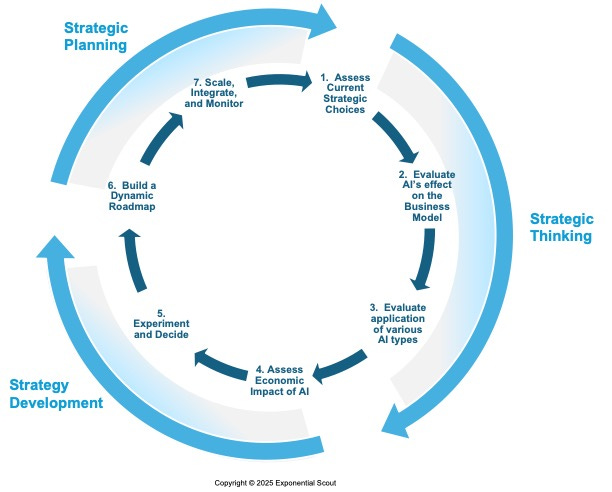
Disciplined Strategy: A Three-Part Process
Many organizations often equate strategy with a static, annual planning exercise. In an era of exponential change, strategy must be dynamic and iterative. Effective and disciplined strategy-making consists of three key activities:
Strategic Thinking: Generating Options
Before making strategic choices, organizations must generate multiple options by assessing AI’s impact on core assumptions, business models, and competitive dynamics.
Strategy Development: Making Trade-Offs
Leaders must determine where AI will create the most value and how it will reshape their "Where-to-Play" (WTP) and "How-to-Win" (HTW) choices.
Strategic Planning: Executing the Choices
AI initiatives must move beyond pilots into full-scale implementation through structured roadmaps and scaled deployment.
The AI-Driven Strategy Redesign Framework
Strategic Thinking: Understanding AI’s Impact on Strategy to Generate Options
Step 1: Map AI to Strategic Choices (PTW Framework)
Executive teams need to evaluate AI’s impact on their current strategy. Roger Martin's Play-to-Win (PTW) framework serves as an excellent tool for assessing how AI will affect an organization’s existing where-to-play (WTP) and how-to-win (HTW) strategic choices.[ii] This step entails articulating the current strategic choices and the original context in which they were made. How will AI challenge industry dynamics, competition, and the fundamental assumptions of the target market? How will it impact our original choices (see diagram below)?
Step 2: Analyze AI’s Impact on the Business Model
The next question is how AI might transform the organization’s business model. The business model reflects a company's strategic choices (WTP and HTW) for creating, delivering, and capturing value. Analyzing the business model allows decision-makers to identify potential AI-driven reinventions and challenge fundamental assumptions. The Exponential Business Reinvention Framework helps leaders assess where AI can redefine operations, transform customer experiences, and reshape value delivery — ultimately generating more precise hypotheses for business model innovation.
Step 3: Evaluate the Various AI Types
Executive teams need to comprehend which type of AI is most relevant to the various aspects of their business model. AI capabilities differ significantly, and organizations must align their strategies accordingly. One of the most valuable frameworks for understanding AI capability progression is Kai-Fu Lee’s Four Waves of AI model, which outlines AI’s evolution in four distinct “waves” (Internet AI, Business AI, Perception AI, and Autonomous AI).[iii] Each wave represents different technological capabilities and business applications—from data-driven personalization to autonomous operations. The OECD Framework for the Classification of AI Systems is also a valuable tool for assessing the application of AI.[iv]
Strategy Development: Making Choices and Testing Assumptions
Step 4: Assessing the Economic Viability of AI
It’s not enough to know where AI will have the most significant impact; the executive team must also identify where the application of AI can be most economically viable. To achieve this, they need to look for areas of tension in the current business model where uncertainty hinders decisions that could drive significant economic value. These points are what the authors of the Prediction Machines refer to as strategic dilemmas. AI should be adopted when it can reduce uncertainty at a low enough cost to influence the decision-making process [v]. AI can decrease uncertainty in three key trade-offs:
Cost vs. Benefit: Does AI create enough efficiency gains to justify investment?
Efficiency vs. Differentiation: Should AI streamline operations or create new, unique value?
Risk vs. Opportunity: How much uncertainty can AI eliminate to enable bold moves?
Step 4 results in a more refined set of WTP and HTW strategic hypotheses, leveraging AI’s capacity to address strategic challenges within the business model. These hypotheses produce various potential business model reinventions, and which ones to pursue will only become apparent once the hypotheses are validated or disproven. These possible reinventions of the business model should be carefully documented in a business redesign grid—one gride version for each potential reinvention.
Step 5: Experimenting with AI Pilots
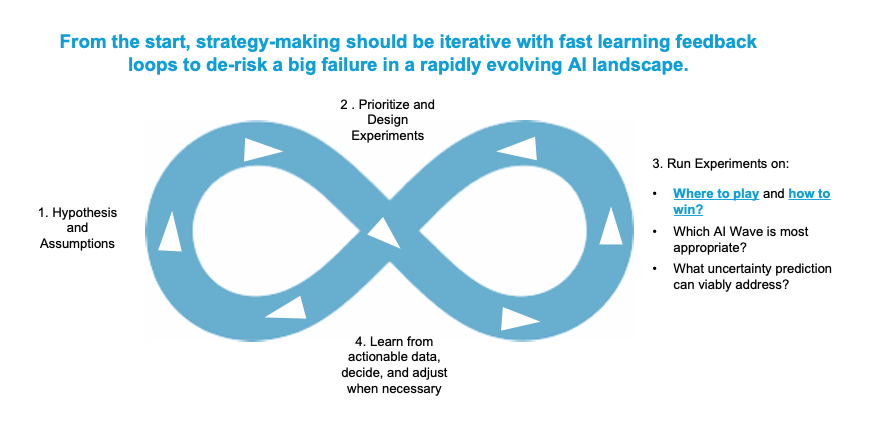
The swift progression of AI renders fixed, long-term strategic plans (like five-year plans) less viable. Capabilities are advancing rapidly, so what appears unattainable now can quickly become achievable. Nevertheless, postponing planning until AI matures might threaten a company’s competitive edge, leaving it exposed when the technology reaches a significant adoption threshold. Strategies should be flexible, nimble, and hypothesis-driven to thrive through the uncertainty of the rapid rate of change.
Organizations should adopt a hypothesis-driven approach to AI, treating each initiative as an experiment with clear success metrics. AI pilots must:
Prioritize high-impact, high-uncertainty initiatives to test new strategic options.
Use an experimentation Kanban to manage AI tests from backlog to execution.
Document learnings to refine the broader AI strategy.
Strategic Planning: Scaling and Executing AI-Driven Strategy
Step 6: Develop a Strategic Roadmap and Flexible Implementation Plan
Executive teams should begin developing flexible and scalable implementation plans alongside the pilot phase. This requires a strategic roadmap prioritizing AI initiatives by readiness and desired strategic outcome, with clear decision points to address the pilots' outcomes. The decision points should include scaling, pivoting the pilot, or stopping. Executive teams should avoid rigid timelines and base their decisions on technology readiness and experimentation results: deployable today, emerging opportunities, and future AI readiness.
Step 7: Scale and Integrate AI Across Operations
Once pilots demonstrate success and the roadmap outlines clear priorities, the organization must transition from experimentation to full-scale AI integration. Scaling AI involves:
Restructuring workflows to integrate AI seamlessly.
Managing workforce transitions by re-skilling employees for AI-augmented roles.
Building governance structures to monitor AI’s long-term impact and compliance.
From Theory to Action: Making AI a Competitive Advantage
AI is not just another IT initiative but a fundamental business transformation. Organizations that fail to rethink their strategy will struggle to compete. To succeed, executive teams must:
Assess AI’s impact on their industry and strategic choices.
Reimagine business models, workflows, and value propositions.
Invest in AI-driven capabilities to sustain differentiation.
Adopt a continuous strategy loop of testing, learning, and scaling.
Want the Full AI and Business Strategy Playbook?
This newsletter is a high-level overview of a more comprehensive framework. To get exclusive access to the complete AI and Business Strategy Playbook—with deeper insights, frameworks, and case studies—subscribe to the paid version of this newsletter.
The AI Business revolution is happening now. Will you lead it or react to it?
From Theory to Action: The AI revolution is happening now. The Exponential Scout aims to help you lead it! Ready to transform your business with AI? Visit my website to schedule a call to discuss reinventing your business model.
[i] Rogers, E. M. (2003). Diffusion of innovations (5th ed.). Free Press.
[ii] Martin, R. (2013). Playing to win: How strategy really works. Harvard Business Review Press.
[iii] Lee, K. (2018). AI superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the new world order. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
[iv] Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). (2022). OECD framework for the classification of AI systems. OECD Publishing. [Available online: https://www.oecd.org/ai/classification/]
[v]Agrawal, Ajay, Joshua Gans, and Avi Goldfarb. (2018) Prediction Machines: The Simple Economics of Artificial Intelligence. Harvard Business Review Press.







This is a great newsletter with fantastic content.